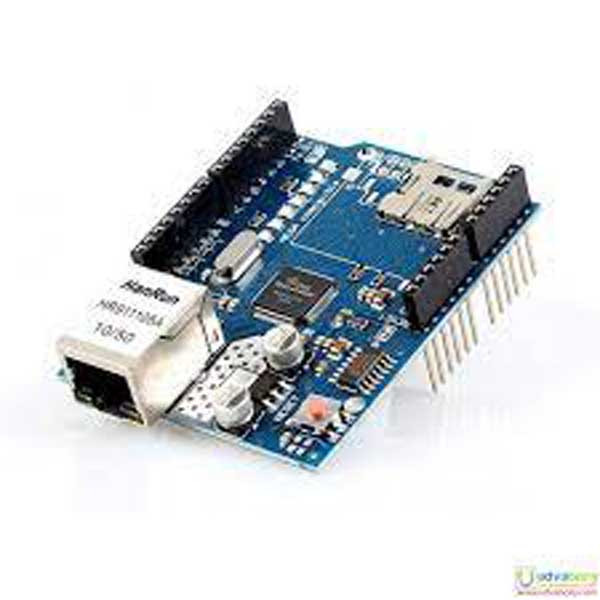
W5100 Ethernet Shield
The Arduino Ethernet Shield allows an Arduino board to connect to the internet. It is based on the Wiznet W5100 ethernet chip providing a network (IP) stack capable of both TCP and UDP. The Arduino Ethernet Shield supports up to four simultaneous socket connections. Use the Ethernet library to write sketches which connect to the internet using the shield.
The ethernet shield connects to an Arduino board using long wire-wrap headers which extend through the shield. This keeps the pin layout intact and allows another shield to be stacked on top..
The latest revision of the shield adds a micro-SD card slot, which can be used to store files for serving over the network. It is compatible with the Arduino UNO and Mega (using the Ethernet library coming in Arduino 0019). An SD card library is not yet included in the standard Arduino distribution.
Arduino communicates with both the W5100 and SD card using the SPI bus (through the ICSP header). This is on digital pins 11, 12, and 13 on the Duemilanove and pins 50, 51, and 52 on the Mega. On both boards, pin 10 is used to select the W5100 and pin 4 for the SD card. These pins cannot be used for general i/o. On the Mega, the hardware SS pin, 53, is not used to select either the W5100 or the SD card, but it must be kept as an output or the SPI interface won't work.
Note that because the W5100 and SD card share the SPI bus, only one can be active at a time. If you are using both peripherals in your program, this should be taken care of by the corresponding libraries. If you're not using one of the peripherals in your program, however, you'll need to explicitly deselect it. To do this with the SD card, set pin 4 as an output and write a high to it. For the W5100, set digital pin 10 as a high output.